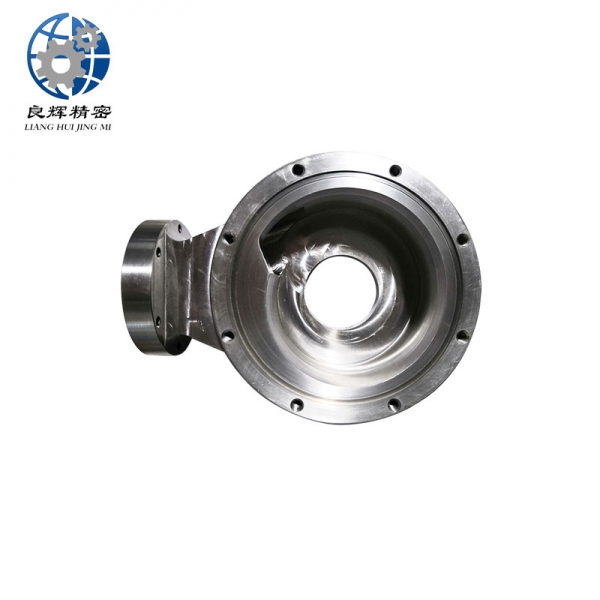
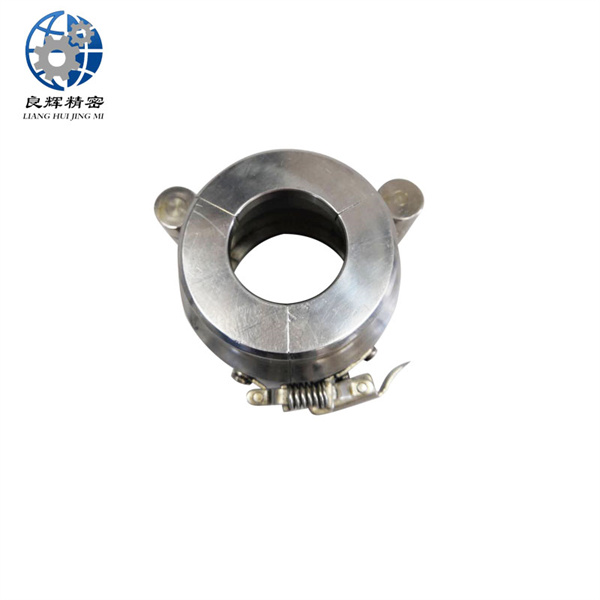
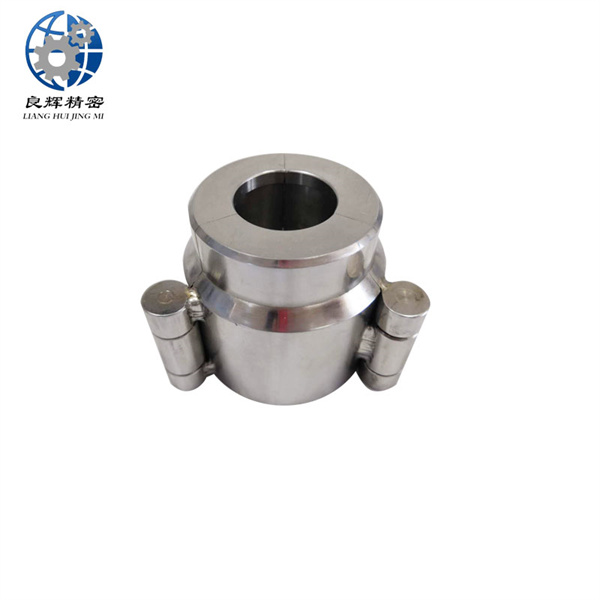
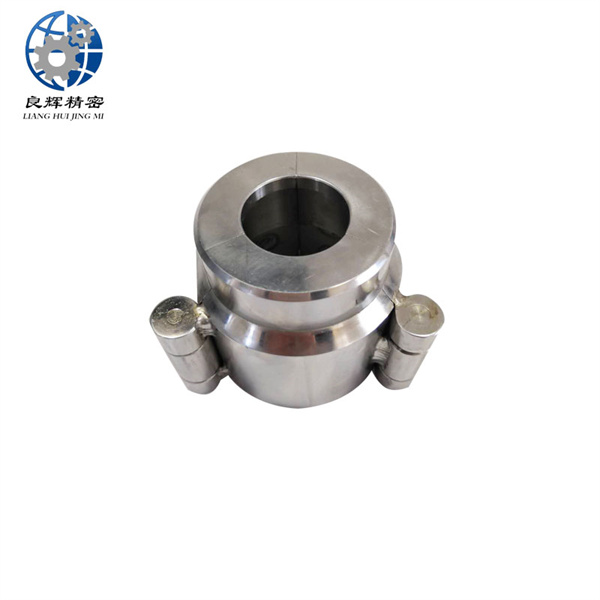
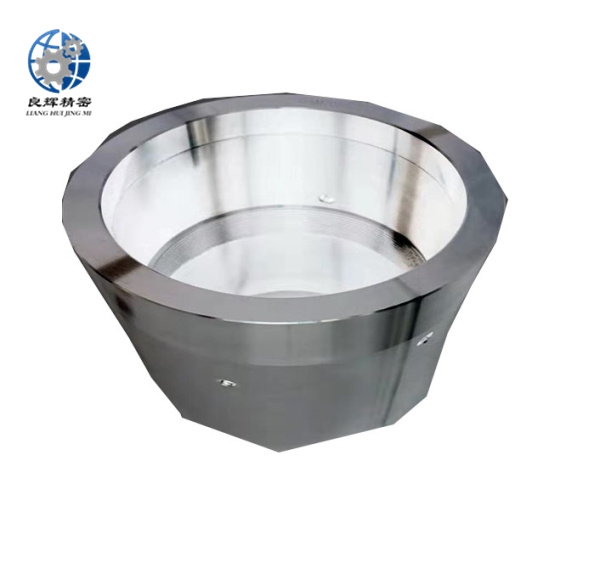
精密機(jī)械加工是在嚴(yán)格控制的環(huán)境條件下,使用精密機(jī)床和精密量具和量?jī)x來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)的。加工精度達(dá)到和超過 0.1微米稱超精密機(jī)械加工。在航空航天工業(yè)中,精密機(jī)械加工主要用于加工飛行器控制設(shè)備中的精密機(jī)械零件,如液壓和氣動(dòng)伺服機(jī)構(gòu)中的精密配合件、陀螺儀的框架、殼體,氣浮、液浮軸承組件和浮子等。飛行器精密零件的結(jié)構(gòu)復(fù)雜、剛度小、要求精度很高,而且難加工材料所占的比重較大。
精密機(jī)械加工的工藝效果是:
①零件的幾何形狀和相互位置精度達(dá)到微米或角秒級(jí);
②零件的界限或特征尺寸公差在微米以下;
③零件表面微觀不平度(表面不平度平均高度差)小于0.1 微米;
④互配件能滿足配合力的要求;
⑤部分零件還能滿足精確的力學(xué)或其他物理特性要求,如浮子陀螺儀扭桿的扭轉(zhuǎn)剛度、撓性元件的剛度系數(shù)等。
Precision machining is achieved using precision machine tools, measuring tools, and instruments under strictly controlled environmental conditions. Precision machining with a processing accuracy of 0.1 microns or more is called ultra precision machining. In the aerospace industry, precision machining is mainly used to process precision mechanical parts in various parts of the actuator control system, such as precision fittings in hydraulic and pneumatic servo mechanisms, frames and shells of gyroscopes, air and liquid floating bearing components, and floats. The structure of precision parts for aircraft is complex, with low stiffness and high precision requirements, and a large proportion of difficult to machine materials.
The process effect of precision machining is:
① The geometric shape and mutual position accuracy of the parts reach the micrometer or arcsecond level;
② The boundary or characteristic dimension tolerance of the parts is below micrometers;
③ The micro roughness of the part surface (average height difference of surface roughness) is less than 0.1 micrometers;
④ Mutual accessories can meet the requirements of mating force;
⑤ Some parts can also meet precise mechanical or other physical property requirements, such as the torsional stiffness of the float gyroscope torsion bar and the stiffness coefficient of the flexible element.