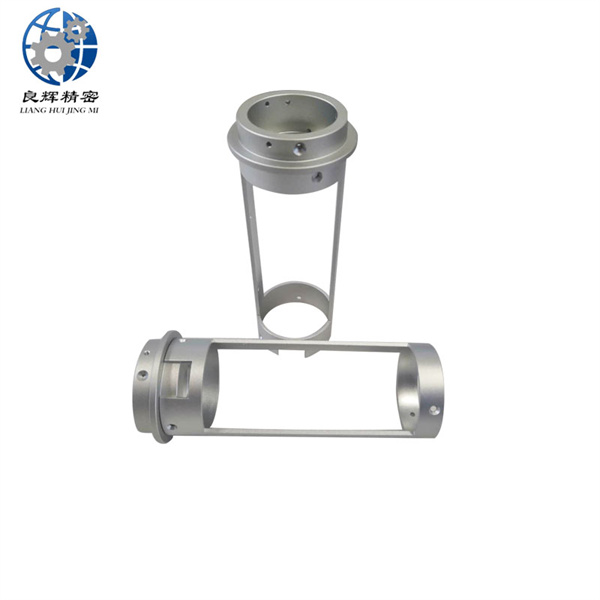
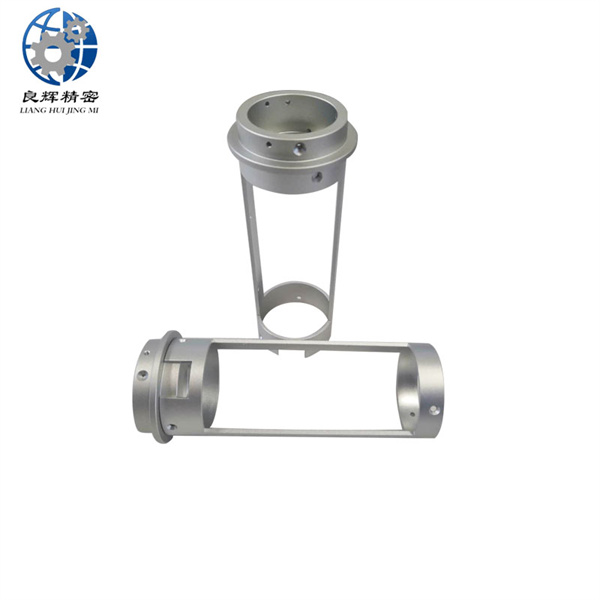
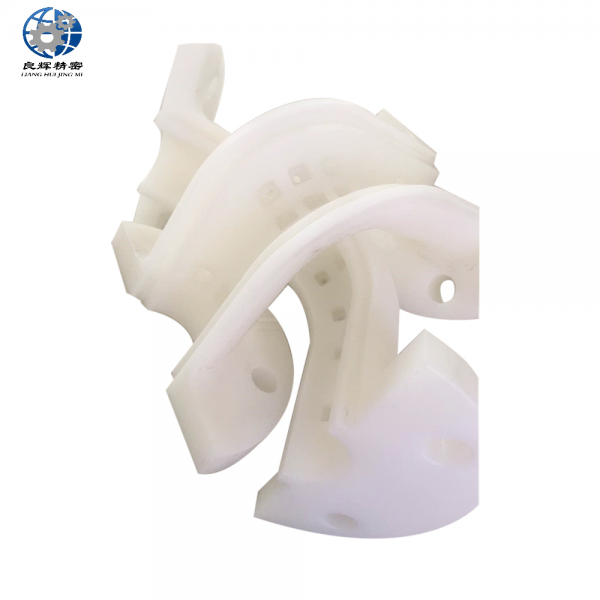
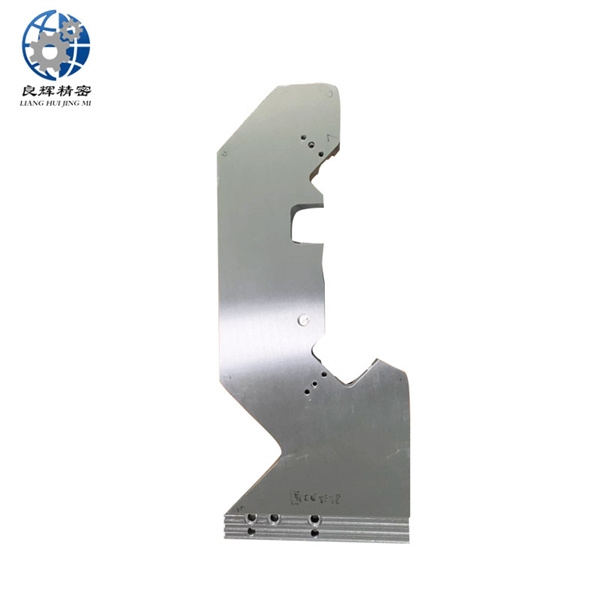
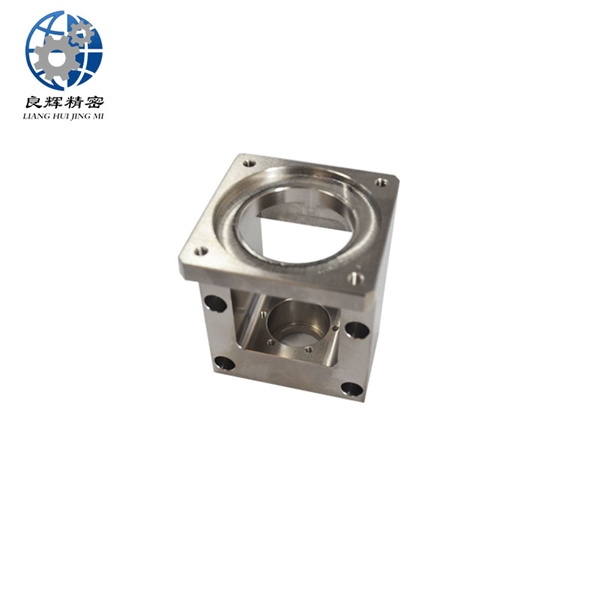
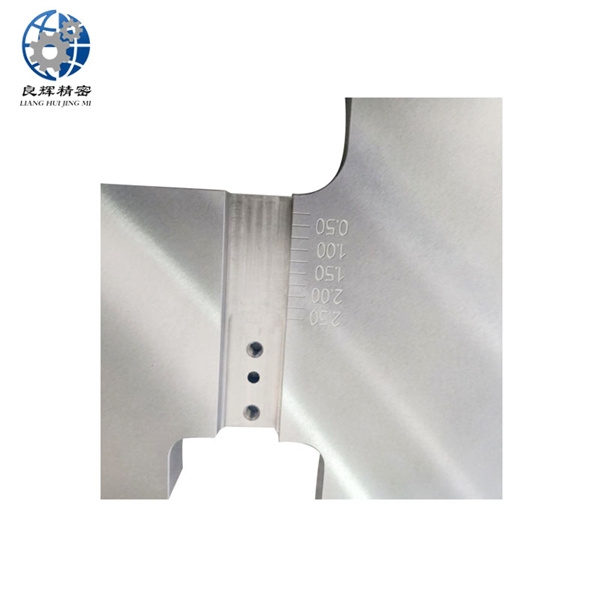
大連精密零部件加工精度是加工后零件表面的實際尺寸、形狀、位置三種幾何參數與圖紙要求的理想幾何參數的符合程度。理想的幾何參數,對尺寸而言,就是平均尺寸;對表面幾何形狀而言,就是絕對的圓、圓柱、平面、錐面和直線等;對表面之間的相互位置而言,就是絕對的平行、垂直、同軸、對稱等。零件實際幾何參數與理想幾何參數的偏離數值稱為加工誤差。
尺寸精度
指加工后零件的實際尺寸與零件尺寸的公差帶中心的相符合程度。
形狀精度
指加工后的零件表面的實際幾何形狀與理想的幾何形狀的相符合程度。
位置精度
指加工后零件有關表面之間的實際位置精度差別。
相互關系
通常在設計機器零件及規定零件加工精度時,應注意將形狀誤差控制在位置公差內,位置誤差又應小于尺寸公差。即精密零件或零件重要表面,其形狀精度要求應高于位置精度要求,位置精度要求應高于尺寸精度要求。
The machining accuracy of precision components in Dalian refers to the degree of conformity between the actual dimensions, shape, and position of the surface of the processed parts and the ideal geometric parameters required by the drawings. The ideal geometric parameters, in terms of size, are the average size; For surface geometry, it refers to absolute circles, cylinders, planes, cones, and straight lines, etc; For the mutual position between surfaces, it refers to absolute parallelism, perpendicularity, coaxiality, symmetry, etc. The deviation between the actual geometric parameters of the part and the ideal geometric parameters is called machining error.
dimensional accuracy
The degree of conformity between the actual size of the processed part and the center of the tolerance zone of the part size. Shape accuracy
The degree of conformity between the actual geometric shape of the machined part surface and the ideal geometric shape.
Position accuracy
The actual positional accuracy difference between the surfaces of the processed parts.
interrelation
Usually, when designing machine parts and specifying the machining accuracy of parts, attention should be paid to controlling the shape error within the positional tolerance, and the positional error should be less than the dimensional tolerance. The shape accuracy requirements of precision parts or important surfaces of parts should be higher than the positional accuracy requirements, and the positional accuracy requirements should be higher than the dimensional accuracy requirements.