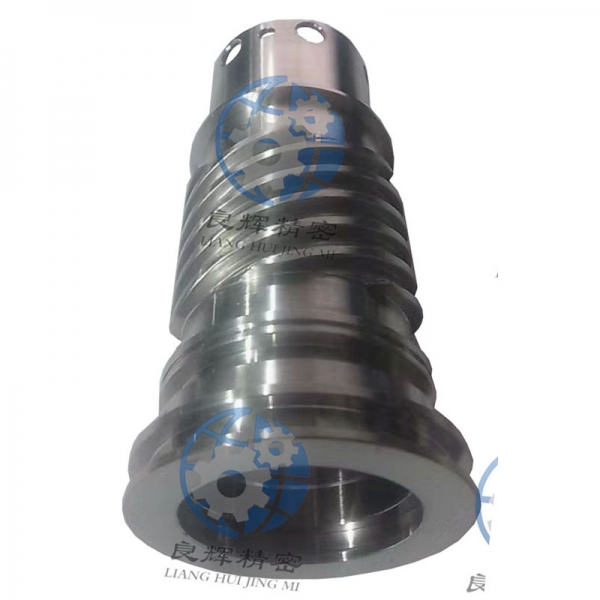
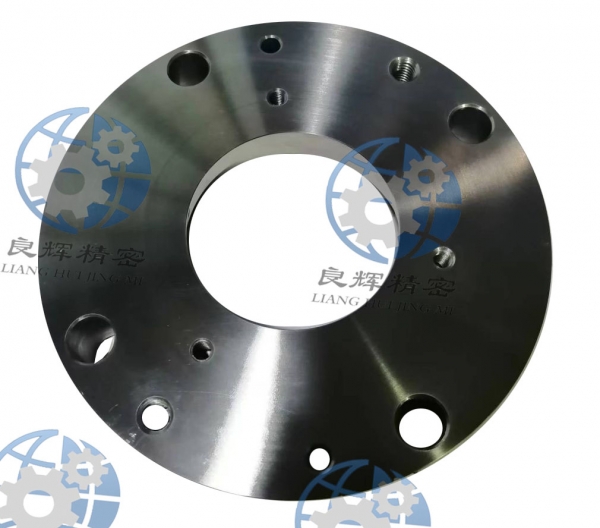
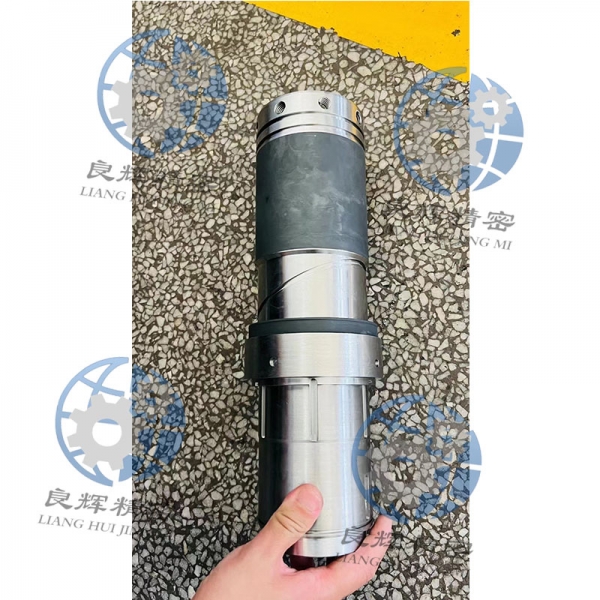
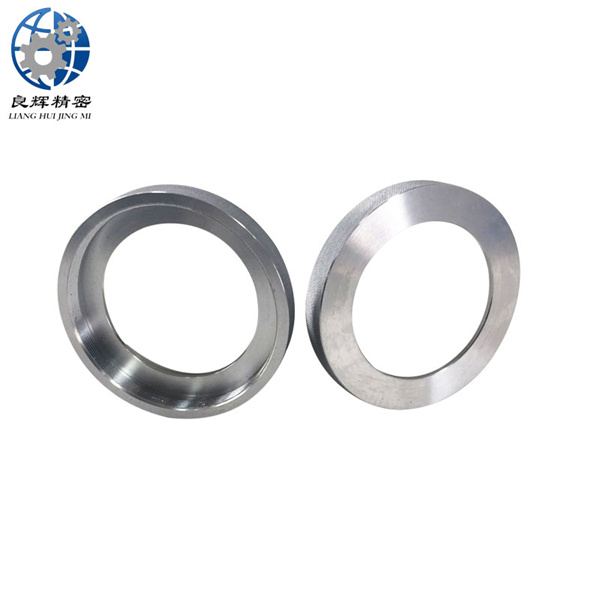
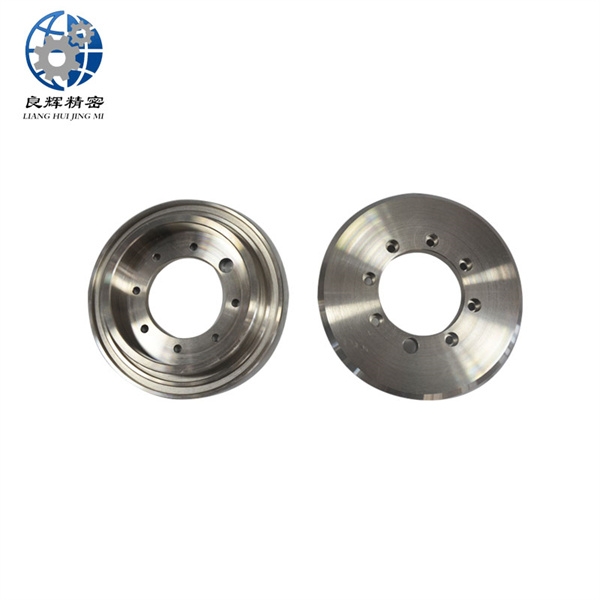
大連數(shù)控加工是指,由控制系統(tǒng)發(fā)出指令使刀具作符合要求的各種運(yùn)動(dòng),以數(shù)字和字母形式表示工件的形狀和尺寸等技術(shù)要求和加工工藝要求進(jìn)行的加工。它泛指在數(shù)控機(jī)床上進(jìn)行零件加工的工藝過(guò)程。
數(shù)控機(jī)床是一種用計(jì)算機(jī)來(lái)控制的機(jī)床,用來(lái)控制機(jī)床的計(jì)算機(jī),不管是專用計(jì)算機(jī)、還是通用計(jì)算機(jī)都統(tǒng)稱為數(shù)控系統(tǒng)。數(shù)控機(jī)床的運(yùn)動(dòng)和輔助動(dòng)作均受控于數(shù)控系統(tǒng)發(fā)出的指令。而數(shù)控系統(tǒng)的指令是由程序員根據(jù)工件的材質(zhì)、加工要求、機(jī)床的特性和系統(tǒng)所規(guī)定的指令格式(數(shù)控語(yǔ)言或符號(hào))編制的。數(shù)控系統(tǒng)根據(jù)程序指令向伺服裝置和其它功能部件發(fā)出運(yùn)行或終斷信息來(lái)控制機(jī)床的各種運(yùn)動(dòng)。當(dāng)零件的加工程序結(jié)束時(shí),機(jī)床便會(huì)自動(dòng)停止。任何一種數(shù)控機(jī)床,在其數(shù)控系統(tǒng)中若沒(méi)有輸入程序指令,數(shù)控機(jī)床就不能工作。機(jī)床的受控動(dòng)作大致包括機(jī)床的起動(dòng)、停止;主軸的啟停、旋轉(zhuǎn)方向和轉(zhuǎn)速的變換;進(jìn)給運(yùn)動(dòng)的方向、速度、方式;刀具的選擇、長(zhǎng)度和半徑的補(bǔ)償;刀具的更換,冷卻液的開(kāi)起、關(guān)閉等。
Dalian CNC machining refers to the machining process in which the control system issues instructions to make the cutting tool perform various movements that meet the requirements, and represents the technical and processing requirements such as the shape and size of the workpiece in the form of numbers and letters. It generally refers to the process of machining parts on CNC machine tools.
Numerical control machine tool is a type of machine tool controlled by a computer. The computer used to control the machine tool, whether it is a dedicated computer or a general-purpose computer, is collectively referred to as a numerical control system. The motion and auxiliary actions of CNC machine tools are controlled by instructions issued by the CNC system. The instructions of the numerical control system are compiled by programmers based on the material of the workpiece, processing requirements, characteristics of the machine tool, and the instruction format (numerical control language or symbols) specified by the system. The numerical control system sends operation or termination information to the servo device and other functional components based on program instructions to control various movements of the machine tool. When the machining program of the part is completed, the machine tool will automatically stop. Any CNC machine tool cannot operate without inputting program instructions into its CNC system. The controlled actions of a machine tool generally include the starting and stopping of the machine tool; The start stop, rotation direction, and speed change of the spindle; The direction, speed, and method of feed motion; Selection of cutting tools, compensation for length and radius; Tool replacement, opening and closing of coolant, etc.